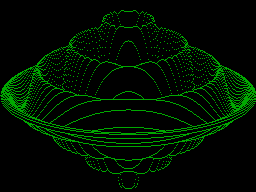
This program plots a three-dimensional view of a surface using high-resolution graphics, To give a solid appearance to the surface, lines which lie behind the surface are not plotted; in other words, the program incorporates 'hidden-line removal'. The function for evaluation is given in line 80 of the two versions of the program, and can be any surface of revolution, in which the height, Q is simply a function of the radius from the centre, R.
As an example, the equation:
Q=(R-1)*SIN(24*R)
where the SIN function gives a rippled effect, and the (R-1) factor causes the ripples to die away towards the edge:
BBC Computer Version
The BBC Computer version uses the medium-resolution graphics mode, with a resolution of 320x256. The origin is set to 640,512, the centre of the virtual graphics screen.
1 REM ... Rotation ...
Set up graphics resolution.
10 MODE 4: VDU 29,640;512;: XS=4: YS=4 20 A=640: B=A*A: C=512
Plot for every X coordinate.
30 FOR X=O TO A STEP XS: S=X*X: P=SQR(B-S) 50 FOR I=-P TO P STEP 6*YS
Calculate R = distance from centre and solve function; Q = height. Give Y coordinate, with correct perspective.
70 R=SQR(S+I*I)/A 80 Q=(R-1)*SIN(24*R) 90 Y=I/3+Q*C
For first point, set maximum and minimum.
95 IF I=-P THEN M=Y: GOTO 110 l00 IF Y>M M=Y: GOTO 130 105 IP Y>=N GOTO 140 110 N=Y
Plot points symmetrically each side of centre.
130 PLOT69,-X,Y: PLOT69,X,Y 140 NEXT I: NEXT X 150 END
Variables:
A - X resolution B - Square of X resolution C - Y resolution I - Distance along X axis M - Highest point plotted N - lowest point plotted Q - height of function R - radius from centre X - X coordinate from centre Y - Y coordinate XS,YS - Virtual points per screen point
Atom Version
The Atom version uses the Atom's highest graphics mode, mode 4, which has a resolution of 256x192. The program needs several changes to work with the Atom's floating-point statements. Floating-point variables prefixed by '%' must be used, although some of the variables are kept as integers since these take only integer values.
The first change is to replace the original program's FOR...NEXT loop by a floating-point DO...FUNTIL loop, so that:
FOR I=-P TO P STEP 6*YS . . NEXT I
in the BBC Computer version becomes:
%I=-%P; DO . . %I=%I+4; FUNTIL %I>=%P in the Atom version.
The IF statements in the BBC Computer version must be changed to FIF statements to ensure that the comparisons are performed on floating-point numbers. Finally, on the Atom we can take advantage of the fact that lower-case labels can be used in GOTO statements instead of line numbers.
1 REM ..ROTATION..
Set up graphics resolution.
10 CLEAR4 20 A=128;B=A*A;C=96
Plot for every X coordinate.
30 FOR X=0 TO A 40 S=X*X; %P=SQR(B-S); %X=-%P
Calculate %R = distance from centre and solve function; %Q = height. Give Y coordinate %Y, with correct perspective.
60 DO %R=SQR(S+%I*%I)/A 80 %Q=(%R-1)*SIN(24*%R) 90 %Y=%I/3+%Q*C
For first point, set maximum and minimum.
95 FIF %I=-%P %M=%Y;GOTOb 100 FIF %Y>%M %M=%Y;GOTOa 105 FIF %Y>=%N GOTOc 110b%N=%Y 115a%Y=C+%Y
Plot points symmetrically each side of centre.
120 PLOT13,(A-X),%Y; PLOTl3,(A+X),%Y 135c%I=%I+4; FUNTIL %I>=%P l45 NEXT X 150 END
Variables:
A - X resolution B - Square of X resolution C - Y resolution I - Distance along X axis %M - Highest point plotted %N - lowest point plotted %Q - height of function %R - radius from centre X - X coordinate from centre %Y - Y coordinate
Further Suggestions
Another function can be obtained by altering lines 80 and 90 of the programs to:
80 Q=COS(R*5)*EXP(-R) 90 Y=I/3-Q*C-5
for the BBC Computer version, or for the Atom:
80 %Q=COS(%R*5)*EXP(-%R) 90 %Y=%I/3-%Q*C-5